7+ Lean process improvement tools to grow your business
Lean process improvement tools can help you to improve quality and efficiency while saving costs. We take a look at seven-plus tools that will help you.
Lean tools identify and eliminate waste in processes.
Tallyfy is Process Improvement Made Easy
Summary
- Value Stream Mapping reveals which steps add value - Map out every step in your process to distinguish activities customers pay for from the seven wastes of lean, then identify redundancies and information flows to find what adds value versus what wastes resources
- Kanban controls effort instead of inventory - Visualize workflows to spot bottlenecks where work piles up, multitasking that reduces focus, waits and delays, excess capacity, and operational issues limiting efficiency, then redirect time so there is always just enough effort to get tasks done
- A3 problem-solving drives root cause analysis - Use this structured approach to clarify problems, analyze causes and effects, implement corrective action, and follow up to ensure solutions stick, all documented on a single sheet (originally A3 paper size) that forces clarity and focus
- Tried and tested tools from Toyota - These Lean process improvement tools achieved Toyota’s success through Kaizen (continuous improvement), evolutionary change rather than revolutionary overhauls, and customer-focused results. Start improving your processes with Tallyfy
You have heard about Lean, the business approach behind Toyota’s success. Achieving more by using fewer resources is just what you want.
You love the idea of Kaizen (continuous improvement), and you’re ready to implement these philosophies into the way you work. It’s time to stock your toolkit with the lean process improvement tools that have taken many a business to the next level.
The beauty of these tools is that they have been tried and tested in practice, so although you may be embarking on something new, it’s ground that others have covered before you. All you need to do is follow the roadmap.
So, let’s jump right in! In this article, we’ll cover 7 of the most popular lean process improvement tools, and explain how to use each.
Value stream mapping
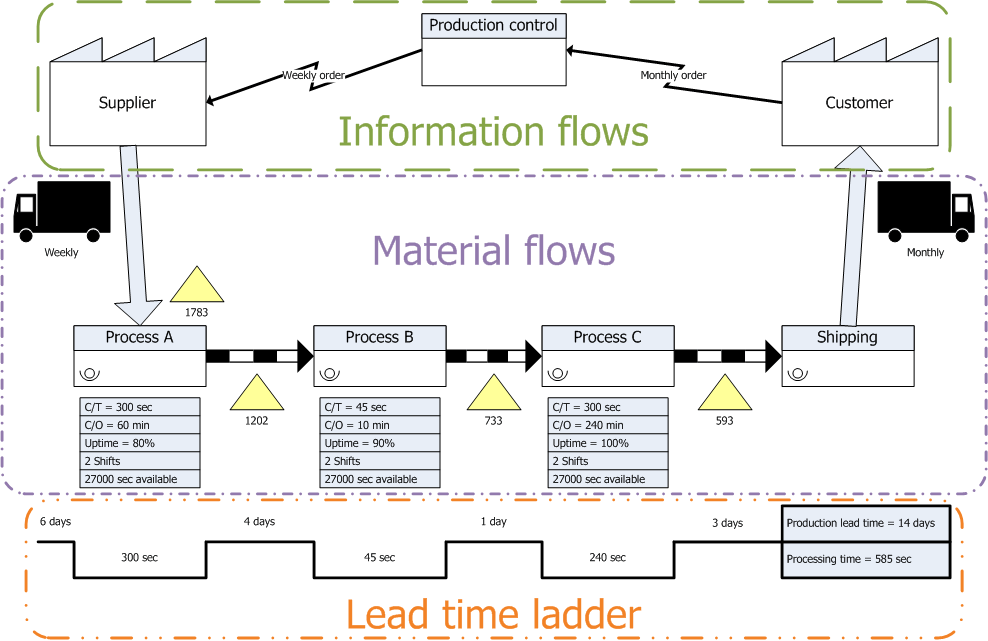 Processes consist of a series of steps, some of which add value, and some of which do not. Of the latter, some are necessary to support the value creation process, and others - well, they might be ready for the cutting room floor!
Processes consist of a series of steps, some of which add value, and some of which do not. Of the latter, some are necessary to support the value creation process, and others - well, they might be ready for the cutting room floor!
You can create a value stream map in order to find which steps are necessary and which ones just waste your resources. What are you looking for?
- What steps does your business follow to deliver a product or service for which people are willing to pay?
- Areas that may be subject to any of the seven wastes of lean.
How to do it:
- Assemble a team and determine what steps you currently follow to create value.
- Identify information flows as well as physical process flows.
- Look for redundancies. If an activity does not add value, does it at least support part of the process?
- Identify interfaces between activities. Later, you will analyze these interfaces to smooth the workflow.
Kanban
It may originally have been developed as a way of controlling the movement of inventory, but Kanban is also a useful lean process improvement tool.
This time, instead of using Kanban to control inventory, you use it to control effort. Your aim is to achieve the best results with the smallest amount of effort needed.
When applying Kanban to process improvement, you begin with the status quo. Your Kanban board is there to help you visualize your workflows.
Now, it’s time to start switching things around and making adjustments. What are you looking for?
- Bottlenecks where work piles up and outcomes are delayed.
- Multitasking that results in waste and reduced focus.
- Waits, delays, and areas where you have excess capacity.
- Operational issues that are limiting efficiency.
- Ways to improve collaboration between employees and departments.
How to do it:
- Begin by setting up the status quo. How does your process work right now?
- Implement continuous, evolutionary change.
- Redirect time and effort so that there is always just enough to get the task done - never too much, and never too little.
- Focus on results from a customer perspective.
Change can be scary, but Kanban helps you to approach it with confidence.
Rather than undergoing revolutionary change in which you might end up trading one set of problems for another, you change things little by little, evaluate the results, and base your next steps on that.
A3 problem-solving
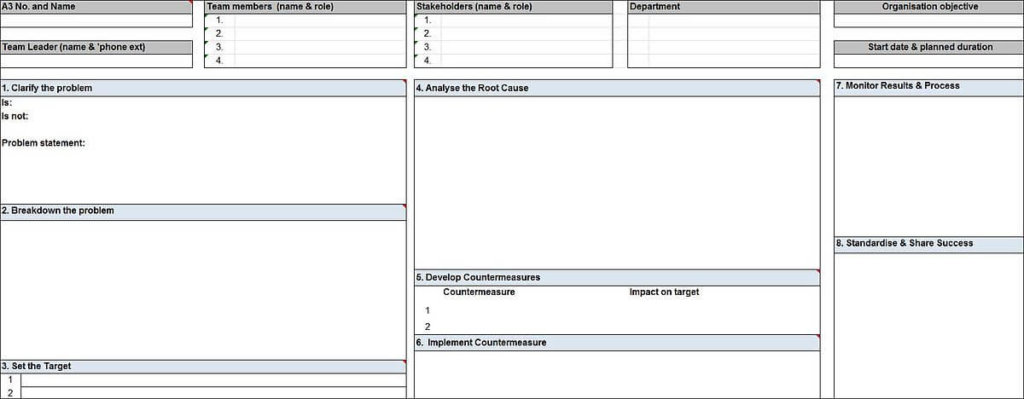
If you think that A3 is really a paper size, you’re quite right! When A3 was first implemented, it used large sheets of paper.
Today, we can implement A3 without the paper, but it still keeps its name. What are you looking for?
- A way to describe a problem you want to tackle.
- Clarification of the problem.
- The real cause of the problem so that you can target it.
- Ways to contain the problem.
- Causes and effects.
- Appropriate corrective action.
- Confirmation that your solution is likely to solve the problem.
- Entrenchment of successful solutions into work routines.
How to do it:
- Capture the theme you are working on.
- Determine the background to the theme.
- Examine the current condition
- Analyze causes.
- Define the target condition.
- Implement the plan.
- Follow up
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle
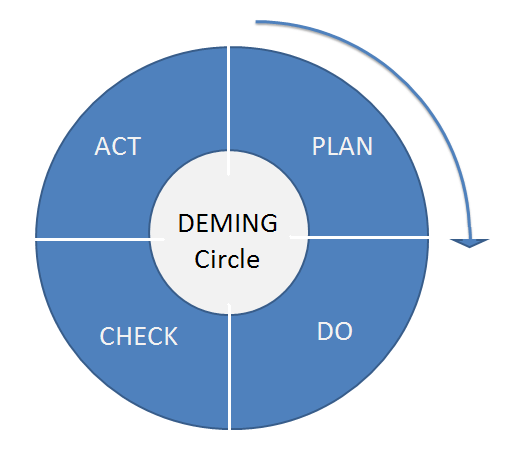 When it comes to processing improvement tools, this one is easy to implement and quick to show results.
What are you looking for?
When it comes to processing improvement tools, this one is easy to implement and quick to show results.
What are you looking for?
- A possible solution to a problem.
- See how your solution works in practice.
- An analysis of results: did the solution work?
- Action: your team adopts the new method.
How to do it:
- Plan: Spot an area that is ripe for improvement and develop a plan to address it.
- Do: Test your new way of working, but only on a small scale.
- Check: Look at hard data to see whether you have achieved the panned results.
- Act: Implement the change and keep checking to be sure you are getting the outcomes you wanted.
- Rinse and repeat: If you did not get the results you wanted, begin the PDCA cycle again. Keep trying till you get the desired results.
Gemba walks
Let’s face it, most of the problems we try to solve in the boardroom do not originate in the boardroom. This process improvement tool takes you to the coalface.
A Gemba Walk is not just a casual stroll through, but a carefully planned and systematically executed process. What are you looking for?
- Opportunities to improve processes from an on-the-ground perspective.
- Input and information from the people who do the real work.
- Any of the seven wastes of Lean.
How to do it:
- Assemble a team so that you can get several perspectives.
- Physically follow processes through from start to finish.
- Ask open-ended questions and gather information.
- Identify possible changes to improve process flows.
- Talk to your team about your findings.
- Implement change.
- Follow it up with another Gemba walk to see whether there is further room for improvement.
Additional lean tools and methods
The 5 Whys
When you are looking to spot problems, root cause analysis might seem like a lengthy process - but the Five Whys give you a shortcut method to dig down to the real reasons why things are not going as planned. What are you looking for?
- The real reasons why a problem occurred.
How to do it:
- Ask why something went wrong.
- Now take the answer and ask why that factor was not as it should be.
- Take your second answer and find the reason why it happened.
- Keep going till you have repeated the “why” question five times.
- Now that you have five reasons that led up to things not going as well as they should, you can start addressing them starting with the fifth why and working back.
Make the necessary process changes to ensure that the problem you encountered does not happen again and monitor the situation to see if you have nailed it.
The 5 Ws and 2Hs (5W2H)
Asking questions is the beginning of knowledge - but it is also a great way to formulate an effective plan of action.
The 5W2H method poses questions, and the answers become the plan to be followed. The 5 Ws stand for what, why, where, when, and who. The two Hs are how (method) and how much (budget). What are you looking for?
- Avoid inertia when launching your process improvement plan.
- Make sure there are no dropped balls or skipped steps.
- Allocate tasks and assign accountability.
- Set up a schedule that everyone understands.
- Be sure everyone understands the parameters within which they will work.
How to do it:
- Determine what needs to be done
- Ensure everyone knows why it must be done.
- Specify where the scene of the action is.
- Decide when actions will occur.
- Indicate who is responsible.
- Specify how it will be done.
- Indicate how much it should cost.
Super-charge your lean process improvement tools with workflow software
Most lean process improvement tools work best if you use them in sync with workflow management software.
While you use lean process improvement tools to spot potential improvements, you can use workflow software to implement these changes and ensure that all your employees are sticking to the new processes. Tools like Tallyfy allow you to…
- Map and tweak your processes on-the-go through the software.
- Spot bottlenecks and hiccups in processes in real time.
- Add, adjust, or remove process steps at will.
- Enforce process execution. The software automatically allocates tasks to relevant employees whenever needed.
- Spot wasted time and effort easily using process analytics.
Combine Tallyfy with other lean process improvement tools and methods to fast-track improvement and ensure that processes are carried out uniformly.
Are you up to the challenge of adopting continuous improvement as part of your business philosophy? It is probably easier than you think. In our experience, organizations that start with value stream mapping tend to identify their biggest wins fastest. One property management team discovered that coordinating tenant transitions across leasing, maintenance, and accounting departments was where most delays occurred. Once they mapped it, they cut turnover times significantly by eliminating handoff bottlenecks between departments.
Related questions
What are the 5 Lean principles of process improvement?
The 5 Lean principles are the foundation of process improvement: define value (what customers really want), map the value stream (understand how work flows), create flow (make work move effectively), establish pull (do only what’s needed), and seek perfection (keep improving). It’s like cleaning a cluttered room: You decide what’s heavy, figure out where things should go, get rid of obstacles, only keep what you need, and continue to tidy up regularly thereafter.
How can I improve my Lean process?
Begin by observing how the work actually happens - not how you think it happens. This matters most. Find the bottlenecks where work accumulates the way water pools behind a dam.
Get advice from the folks doing the work - they frequently know what is hindering them. Use basic visualization tools like sticky notes on a wall to monitor progress. Manufacturing represents about 8% of our conversations at Tallyfy, and small incremental improvements win out over big dramatic changes that do not last. Teams who commit to one improvement per week outperform those who attempt quarterly overhauls. Feedback we have received suggests that organizations managing 50 or more active workflows simultaneously are the ones that benefit most from Kanban-style visualization, because the sheer volume makes mental tracking impossible.
What are the five fundamental tools of Lean?
The primary Lean tools are 5S (sort, set in order, shine, standardize, sustain), visual management (making work transparent), standardized work (best known way), mistake-proofing (error proofing), and continuous flow (work flowing smoothly). These are to a cyclist what a hammer and saw are to a carpenter - each with its specific use, but used most effectively in concert.
What are the benefits of lean process improvement?
Lean improvements mean happier customers, less beleaguered employees and better financial results. Work gets done faster and with fewer errors, costs fall as waste vanishes, and people spend less time fighting fires and more time doing valuable work. It’s like going from a clunky old computer to a new one - it’s an upgrade.
How do you identify waste in a process?
Seek the eight wastes: waiting, overproduction, rework, motion, processing, inventory, transport, and unused creativity. Keep an eye out for people waiting for approvals, making extra copies, redoing work, having unnecessary meetings or supplies that are just sitting there. These wastes are a hole in the bucket and they drip, drip, drip away time and money.
What is the difference between Lean and Six Sigma?
Lean is about eliminating waste, and making work flow smoothly, while Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation and defects. Lean would be like cleaning out a cluttered garage, Six Sigma would be like calibrating a sophisticated instrument. They are really complementary - Lean makes processes easier, and Six Sigma makes processes more consistent.
How do you measure the success of Lean improvements?
Track simple metrics that customers and workers care about: the length of time things take, the frequency of errors, the cost of things and how much people like them. Steer clear of the kind of arcane measurements that nobody gets. It is like monitoring your fitness - concentrate on simple readings, like weight and energy level, rather than dense analyses of body composition.
What role do employees play in Lean process improvement?
Employees are the key to Lean improvement - they are those that know most about the work and who will usually have the best ideas of how to make it better. They should be comfortable identifying issues and offering solutions. Think of it as a neighborhood watch - the people who live there know best what must be fixed and how.
How do you sustain Lean improvements over time?
Form habits and systems that make the new way easier than the old. Establish visible cues, regular check-ins and clear criteria. Ensure that leaders are behind the changes and acknowledge good efforts. It’s like eating a healthy diet - you want to make it part of your normal routine, not just a quick fix.
What are common mistakes in implementing Lean tools?
Some of the most common mistakes involve trying to do too much too fast, putting tools over people, failing to engage everyone affected by changes, and expecting immediate results. Don’t mimic solutions of other businesses without understanding what you need. Remember, Lean resembles gardening more than construction - it requires constant nourishment and time to grow.
About the Author
Amit is the CEO of Tallyfy. He is a workflow expert and specializes in process automation and the next generation of business process management in the post-flowchart age. He has decades of consulting experience in task and workflow automation, continuous improvement (all the flavors) and AI-driven workflows for small and large companies. Amit did a Computer Science degree at the University of Bath and moved from the UK to St. Louis, MO in 2014. He loves watching American robins and their nesting behaviors!
Follow Amit on his website, LinkedIn, Facebook, Reddit, X (Twitter) or YouTube.

Automate your workflows with Tallyfy
Stop chasing status updates. Track and automate your processes in one place.