What is Lean Six Sigma - Benefits and Implementation
Combine lean thinking with six sigma methodology to eliminate waste and achieve near-perfect processes
Summary
You do not need a Black Belt certification or complex flowcharts to start fixing this mess. Actually, the traditional approach might be part of the problem.
- The uncomfortable truth about traditional implementations
- Lean Six Sigma combines waste elimination (Lean) with defect reduction (Six Sigma) to achieve near-perfect processes - just 3.4 defects per million opportunities
- Real results from operations teams: 64% reduction in onboarding time (14 days to 5), 75% faster processing times, and one professional services firm cut costs by $1M while growing revenue 4x with 75% fewer staff
- Based on hundreds of workflow implementations, we have seen that traditional BPM tools with complex flowcharts often make things worse - modern teams need simpler, actionable approaches
- Teams consistently report the same pattern: process fragmentation across 4-5 tools (spreadsheets, WhatsApp, Asana, email) creates 60% of their waste before any improvement even starts
Imagine news of a plane crash every single week. Picture the Post Office losing 1,600 pieces of mail yearly. Or opening any book to find two spelling errors per page.
Sounds unacceptable, right? Yet most mid-size companies accept similar failure rates in their daily operations. That invoice that took 3 weeks to approve? The customer onboarding that somehow stretched to 47 days? These are not just annoyances - they are symptoms of processes that desperately need Lean Six Sigma thinking.
Here is what nobody tells you though: You do not need a Black Belt certification or complex flowcharts to start fixing this mess. Actually, the traditional approach might be part of the problem.
What is Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma combines two powerful ideas:
- Lean: Eliminate waste in your processes
- Six Sigma: Reduce defects to near zero
The magic number? 3.4 defects per million opportunities. Sounds impossible? Amazon processes millions of orders hitting close to this standard. According to US Army reports, their Lean Six Sigma program saved over $2 billion. Your local hospital's surgical team achieves similar standards - because they have to.
But here is the thing: You do not need to be Amazon to benefit. Even reducing defects by 50% can transform your operations.
Think of it this way: A mid-size accounting firm in Chicago used basic Lean Six Sigma principles to cut tax return processing from 14 days to 3. No consultants. No complex software. Just systematic improvement.
The difference between Lean and Six Sigma? Lean asks "Is this step necessary?" while Six Sigma asks "Can we do this step perfectly every time?" Together, they are unstoppable.
The uncomfortable truth about traditional approaches
Let us address the elephant in the room. You have probably seen Lean Six Sigma implementations that look like this:
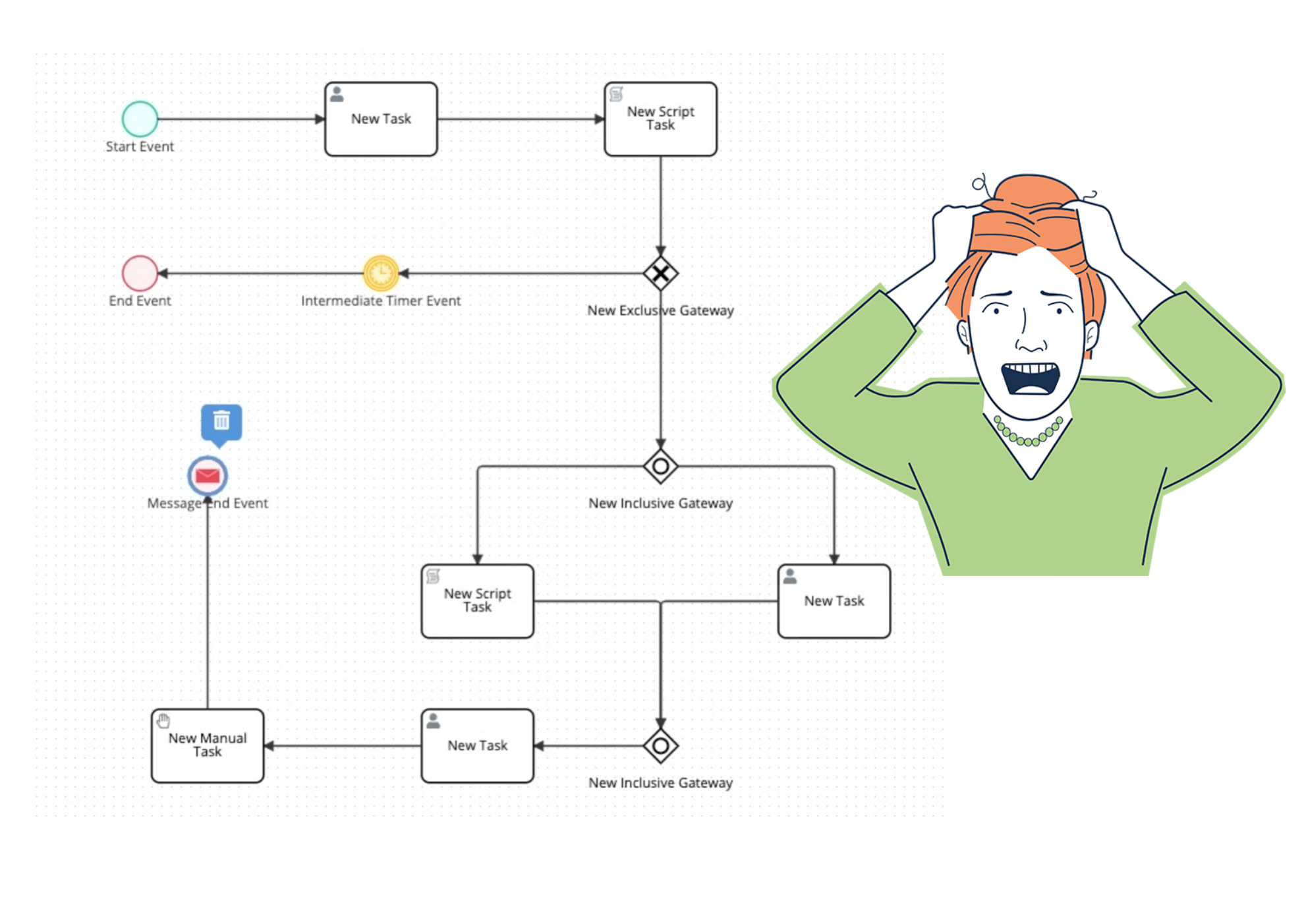
See that mess? That is supposedly going to help your team work better. Except it will not. Because while you are drawing boxes and arrows, your competitors are actually fixing their processes.
Here is what research shows: According to industry analysis, 60% of Six Sigma projects fail. Another 40-60% of Lean projects never achieve their goals. The reason? They get bogged down in complexity that looks impressive in PowerPoints but falls apart in reality.
We have seen this pattern repeatedly with large organizations. One multinational enterprise with over 100 entities across 50 countries wanted to standardize their approval process. Their pain? Manual approvals via email were impossible to track, questions during approval processes got lost, and retrieving historical decisions required digging through years of email chains. The solution was not a complex BPM implementation - it was a simple, trackable workflow that anyone could follow without specialized training.
Jack Welch, former CEO of General Electric, wrote in his 2005 book "Winning" that variation is evil. But you know what else is evil? Complexity that prevents people from actually improving anything.
The eight wastes destroying efficiency
Lean identifies eight types of waste. Let us look at each with examples you will actually recognize:
1. Defects - Things done wrong
Manufacturing example: A medical device company ships 100 units. 7 get returned for quality issues. Each return costs $2,000 to process.
Service example: Your sales team sends proposals with pricing errors 15% of the time. Result? Lost deals and damaged credibility.
The fix: Build quality checks into the workflow itself, not after the fact.
2. Overproduction - Making stuff nobody wants
Real scenario: A marketing team creates 50 blog posts monthly because "content is king." Analytics show only 3 get meaningful traffic.
The waste: 47 pieces of content that consumed resources but delivered zero value.
Better approach: Produce less, but make it exceptional. Quality beats quantity every time.
3. Waiting - The productivity killer
Picture this: Your invoice sits in someone's inbox for 8 days. They spend 5 minutes approving it. That is 99.9% waiting, 0.1% actual work.
Healthcare example: Patients wait 45 minutes for a 10-minute consultation. The doctor's expertise is wasted on scheduling inefficiencies.
Simple solution: Automated routing and notifications eliminate most waiting.
4. Non-utilized talent - Your smartest people doing dumb tasks
Your $150k/year engineer spending 2 hours weekly on expense reports? That is $15,000 annually in wasted expertise.
Common offenders:
- Senior staff doing data entry
- Specialists handling admin work
- Managers chasing status updates
A diagnostics company we worked with had their scientists manually tracking drug release processes when they should have been doing research. Their process improvement project identified over 60 workflows that were consuming expert time on routine approvals and status tracking. A global consumer goods company had similar issues: their project management and operations teams - 163 people costing over $11 million annually - were stuck doing redundant coordination work instead of strategic activities.
The answer: Automate the mundane so humans can do human work.
5. Transportation - Moving things unnecessarily
Physical example: Parts traveling between 5 different departments, accumulating 2 miles of internal transport.
Digital example: Documents bouncing between 7 email inboxes before approval. Each transfer adds delay and risk.
Modern fix: Centralized digital workflows where work comes to people, not vice versa.
6. Inventory excess - Too much stuff sitting around
Manufacturing: $2 million in parts gathering dust in warehouses.
Services: 200 support tickets in the backlog, half of which are no longer relevant.
The principle: Work-in-progress is a liability, not an asset. Finish what you start before starting more.
7. Motion waste - Unnecessary movement
Ever watched someone click through 6 screens to update one field? Or walk to three offices for signatures? That is motion waste.
Digital motion waste:
- Switching between 8 different apps
- Copy-pasting the same data repeatedly
- Re-entering information already captured
Solution: Integrate systems so data flows automatically.
8. Extra-processing - Doing more than required
Classic example: Creating beautiful 47-slide presentations nobody reads past slide 3.
Modern version: Building complex Excel trackers when a simple checklist would work better.
The test: If removing a step does not affect the outcome, that step is waste.
Real benefits from real companies
Let us move beyond the famous examples everyone quotes. Yes, General Electric saved $12 billion under Jack Welch. But what about companies like yours?
Mid-size company wins
Feedback we have received from operations teams consistently points to similar patterns. Here are examples that match what we see:
A professional services firm (started with 65 employees): Achieved $1 million in Year 1 savings and 4x revenue growth by documenting and enforcing SOPs. The real surprise? They operated with 75% fewer staff afterward because they eliminated redundant and outdated tasks that nobody realized were wasting resources.
A payroll processing company (11-50 employees): Onboarding time dropped from 14 days to 5 days - a 64% reduction. The fix was not complex: they built quality assurance controls into document collection and eliminated manual follow-ups for missing information.
A legal firm (10+ employees): Doubled the number of cases each attorney could manage by replacing Excel spreadsheets with structured process templates. Attorneys were previously required to memorize 100+ steps for estate proceedings - now those steps are systematized.
A property management company (managing 3,500+ properties): Achieved 75% faster processing times for maintenance and tenant renewals. Their starting point? Work was scattered across Salesforce, Trello, Airtable, DocuSign, and email with unclear accountability.
The multiplier effect
Here is what the case studies do not always mention: The biggest benefit is not the direct savings. It is what happens next:
- Employee morale improves when they stop fighting broken processes
- Customer loyalty increases when you deliver consistently
- Innovation accelerates because you are not firefighting constantly
The Ohio food bank case documented by ASQ that cut delivery time from 92 to 39 days? They are now targeting 20 days. Success breeds ambition.
Why simple beats complex for continuous improvement
Complex BPM systems promise everything but require:
- Months of implementation
- Expensive consultants
- Extensive training
- IT department involvement
- Ongoing maintenance headaches
Meanwhile, teams using simpler workflow tools:
- Go live in days
- Train themselves in hours
- Make improvements instantly
- Actually enjoy using the system
Which approach do you think succeeds more often?
How to implement without the complexity
Forget the traditional approach. Based on hundreds of workflow implementations we have supported, here is how modern teams do it:
Pick ONE process that drives everyone crazy
Not your most complex process. Not your most important. Pick the one that makes people say "Why is this so difficult?"
Common winners:
- Employee onboarding
- Invoice approvals
- Customer support ticket routing
- Marketing approval workflows
- IT equipment requests
Then map what actually happens
Do not draw flowcharts. Instead, document the real steps:
- Who does what?
- How long does each step take?
- Where do things get stuck?
- What information gets lost?
Pro tip: The process is always worse than management thinks.
Apply DMAIC (simplified version)
Define: What is the specific problem? "Invoices take too long" is vague. "Invoices average 21 days for approval" is specific.
Measure: Gather real data. How many invoices? Average time? Where is the bottleneck?
Analyze: Usually, 80% of delays come from 20% of the steps. Find those steps.
Improve: Start with the easiest fixes:
- Eliminate redundant approvals
- Automate notifications
- Create clear escalation paths
- Set up parallel processing where possible
Control: This is where most fail. You need ongoing monitoring to ensure improvements stick.
The secret weapon: Start with templates
Do not reinvent the wheel. Most processes follow patterns:
- Approval workflows
- Review and feedback cycles
- Handoff sequences
- Quality check gates
Use proven templates and customize them. You will implement in days, not months.
Your practical next steps
If you are just starting:
- First: Pick your most annoying process. Just one.
- Then: Document what really happens (be honest)
- Next: Identify the biggest bottleneck
- After that: Fix that ONE thing
- Check: Measure the improvement
- Repeat: Pick your next process
If you have tried before and failed:
The problem was not Lean Six Sigma. The problem was probably:
- Too much complexity
- Lack of ongoing support
- No simple tools to sustain changes
- Trying to fix everything at once
Start smaller this time. Use modern DMAIC approaches that do not require a PhD.
If you are ready to scale:
Once you have fixed 2-3 processes manually, it is time for tools that scale. Look for:
- Template libraries so you do not start from scratch
- Analytics built-in to spot bottlenecks automatically
- Integration capabilities to connect your existing tools
- Change management features to roll out improvements smoothly
The continuous improvement loop that actually works
- Run the process using simple, clear steps
- Spot problems through actual usage (not theory)
- Gather feedback via comments right in the workflow
- Make small improvements without breaking everything
- Measure the impact with real data
- Repeat
This is how operations teams consistently achieve results. One dental practice reduced appointment scheduling from 15 minutes to 3. Not through complex reengineering, but through continuous small improvements.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between Lean and Six Sigma?
Lean focuses on eliminating waste and improving flow - making things faster and more efficient. Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation and defects - making things more consistent and higher quality. Lean Six Sigma combines both: remove what does not add value, then perfect what remains. Think of Lean as "doing the right things" and Six Sigma as "doing things right."
Do I need to get certified in Lean Six Sigma?
Not necessarily. While certifications (Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt) provide structured learning, many successful implementations happen without formal certification. If you are implementing basic improvements in a mid-size company, practical experience and the right tools matter more than certificates. However, having at least one certified team member can help guide more complex projects.
How long does a typical Lean Six Sigma project take?
Despite what consultants might tell you, most impactful projects should take 4-6 months maximum. If it is taking longer, you are probably trying to boil the ocean. Start with 30-60 day pilot projects to build momentum. Based on hundreds of implementations, the most successful teams see first improvements within 2-3 weeks of starting.
What is the biggest mistake companies make with Lean Six Sigma?
Trying to fix everything at once. The second biggest? Using tools that are more complex than the problems they are solving. Companies often invest in enterprise BPM systems that require months of setup when simple workflow automation would deliver results in days. Focus on quick wins first, then expand.
Can Lean Six Sigma work for service industries?
Absolutely. In fact, service industries often see faster results because their "inventory" is often just information waiting in queues. Law firms reduce contract review time by 70%. Healthcare providers cut patient wait times in half. Marketing agencies streamline campaign approvals. The principles translate perfectly - waste is waste, whether it is physical parts or digital documents.
How much does Lean Six Sigma implementation typically cost?
Traditional consulting-led implementations can run enterprise-level budgets for mid-size companies. But here is the secret: You do not need that. Start with one process, use simple tools, and expand based on results. Many companies achieve significant improvements for less than the cost of one consultant's monthly fee. The real cost is not money - it is continuing to operate with broken processes.
What if my team resists the changes?
Resistance usually comes from fear of complexity or job security concerns. Counter this by: Starting with volunteers who are frustrated with current processes, showing quick wins to build confidence, making changes that actually make their jobs easier (not harder), and being transparent that the goal is to eliminate boring work, not people. When people see that Lean Six Sigma makes their day better, resistance melts away.
How do I maintain improvements long-term?
This is where 60% of projects fail - the improvements do not stick. Success requires: Built-in monitoring that does not require extra effort, regular (but brief) review cycles, easy ways to suggest and implement improvements, and tools that make the improved process easier than the old way. If the new process requires more discipline than the old one, it will fail.
Is Lean Six Sigma outdated?
The principles are timeless - reducing waste and variation will always matter. What is outdated is the traditional implementation approach with complex flowcharts and lengthy consulting engagements. Modern Lean Six Sigma leverages AI and automation to identify improvements and implement changes faster than ever.
Can small teams use Lean Six Sigma?
Small teams often see the best ROI from Lean Six Sigma because they cannot afford waste. You do not need a dedicated quality department. You need clear processes, simple tools, and a commitment to continuous improvement. In our conversations with operations teams, some of the most impressive results come from companies with fewer than 50 employees.
What is the most common root cause of process waste?
Based on hundreds of workflow implementations we have supported, tool fragmentation is the top culprit. Teams typically have their work scattered across 4-5 different systems - spreadsheets, messaging apps like WhatsApp or Slack, project tools like Asana or Trello, plus email. One property management team we spoke with had processes split across Salesforce, Trello, Airtable, DocuSign, and email simultaneously. Just consolidating into a single workflow system delivered 75% faster processing times before any formal Lean Six Sigma analysis even began.
How do I know if process standardization is worth the effort?
Look for this telltale sign: the same task takes dramatically different amounts of time depending on who does it. We have seen teams where the same onboarding process took some employees 5 days while others took 14 days. When attorneys in a legal firm needed to memorize 100+ steps for case proceedings, errors and missed tasks were constant. After documenting and systematizing those steps, the firm doubled their case capacity per attorney. If your experienced staff cannot take a vacation without everything falling apart, you have a standardization problem worth solving.
The bottom line
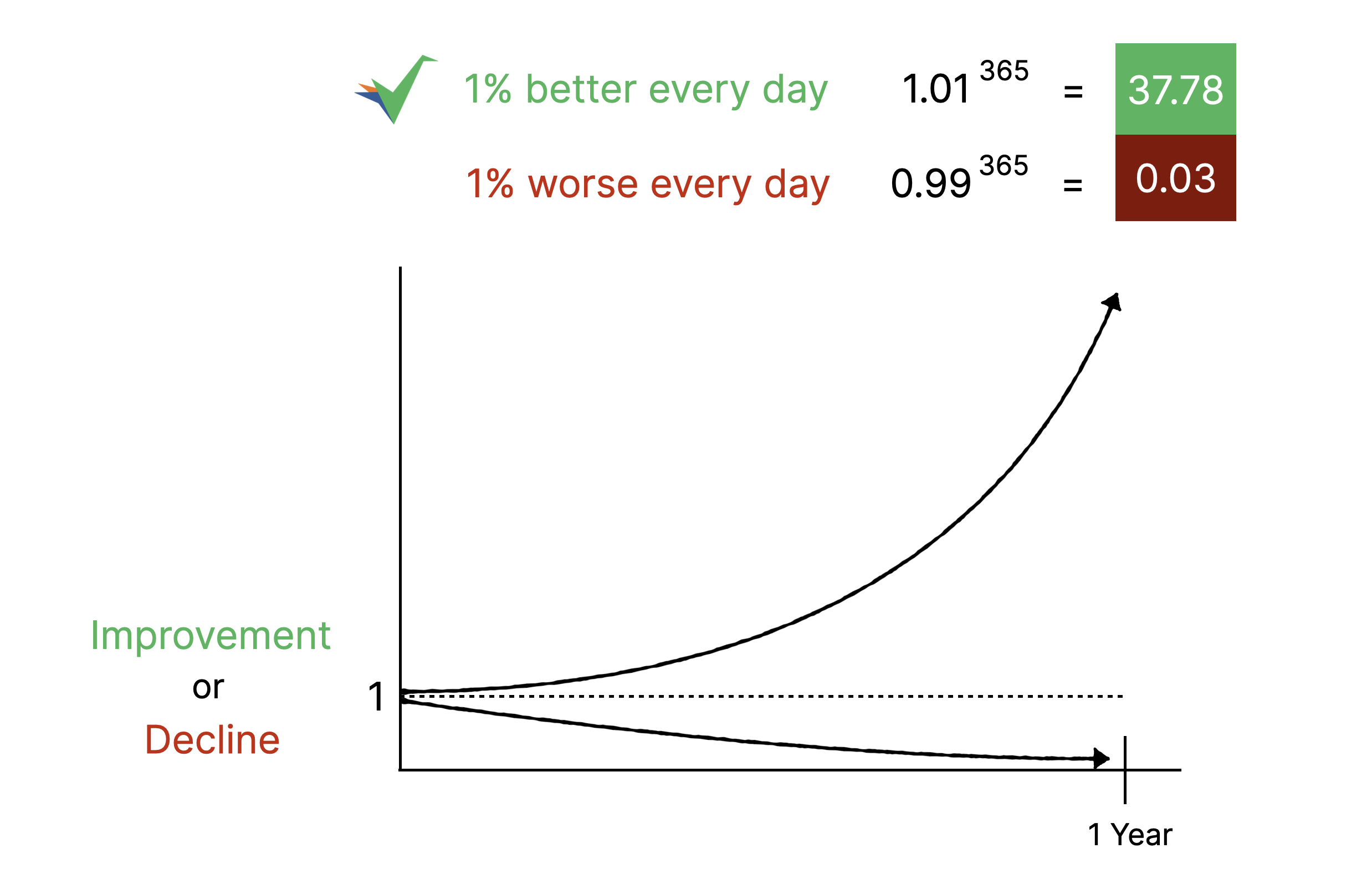
Lean Six Sigma is not about perfection. It is about being slightly better today than yesterday, consistently. That compounds into dramatic results.
You have seen the theory. You have heard the success stories. But nothing changes until you pick one broken process and fix it.
Start this week. Choose something specific - invoice approvals, customer onboarding, employee time-off requests. Document what actually happens. Find the biggest bottleneck. Fix it. Measure the improvement.
That is it. That is how billion-dollar transformations begin.
Ready to streamline your workflows?
See how Tallyfy makes workflow management simple and effective for teams of all sizes.
About the Author
Amit is the CEO of Tallyfy. He is a workflow expert and specializes in process automation and the next generation of business process management in the post-flowchart age. He has decades of consulting experience in task and workflow automation, continuous improvement (all the flavors) and AI-driven workflows for small and large companies. Amit did a Computer Science degree at the University of Bath and moved from the UK to St. Louis, MO in 2014. He loves watching American robins and their nesting behaviors!
Follow Amit on his website, LinkedIn, Facebook, Reddit, X (Twitter) or YouTube.