How to use deep learning in business
There are a lot of deep learning business applications, some of which are still in development. Learn how companies use deep learning today!
Summary
- Deep learning uses artificial neural networks to process massive data sets - Systems score and classify information through binary logic, then improve accuracy as they process more data and remember patterns from previous entries
- Already powering major consumer applications - Netflix content recommendations, Facebook image classification (as of 2016) showing detected tags, Google Translate accuracy improvements, and self-driving cars from Volkswagen (as of 2017) and Google Waymo
- Medical applications in development promise major breakthroughs - Improving diagnosis accuracy beyond current 10-20% error rates, creating gene-tailored medicine for individual genetic makeups, and helping blind people navigate through camera-equipped headsets. Explore Tallyfy automation features
There are many Deep Learning business applications, with new opportunities emerging regularly. What was once a futuristic concept is now found in day-to-day services everyone uses.
With deep learning, we’re seeing an explosion of platforms that are self-teaching and autonomous, paving the way for new kinds of business models and revolutionizing current industries. The pace is staggering.
What is deep learning?
You might think that Deep Learning sounds a lot like Artificial Intelligence, and that is true to a point.
Artificial Intelligence is a machine developed with the capability for intelligent thinking. Then, Machine Learning is a means of achieving AI: letting the computer parse a large amount of data and learn from it.
Deep Learning, by contrast, is an approach to Machine Learning which involves Artificial Neural Networks to work with the data.
Today, there are more Deep Learning business applications than ever. In some cases, it is minor benefits for the company, such as teaching the system to identify images. In others, it can be the core offering of the product, such as self-driving cars.
How does deep learning work?
Deep Learning is based on processing data - a LOT of data. The data is fed through a neural network where every piece of information is scored based on binary data or simple true/false questions.
The data is then classified according to how it is scored or the answers received by the logic network. In our conversations with CTOs at technology companies exploring automation, most significantly underestimate how much training data they need for accurate results - often by an order of magnitude.
Image processing is a perfect example of how Deep Learning is being used in the real world. Imagine a checkpoint set up to record not only the number of vehicles that pass a specific location but also their exact model.
The outline and shape of those vehicles are fed into the system where there is already a database trained at detecting the vehicle types. It compares the shapes it sees to its database and, with some measure of good accuracy, classifies the cars in a split second.
The deep learning comes into play as the computer continues to do its job. The more data it gets to work with, the better it gets at classifying vehicles, as it remembers the previous entries.
While deep learning handles the complex pattern recognition, most businesses also need straightforward workflow automation for their day-to-day processes. Not every task requires neural networks - sometimes you just need reliable, trackable workflows.
Workflow Automation Software Made Easy & Simple
Deep learning business applications
Over the past few years, Deep Learning has been becoming more and more common. It can be found powering some of the most powerful tech today: everything from entertainment media to self-driving cars.
Content recommendation
One of the most common deep learning applications is seen with content recommendations at Netflix.
Deep learning is used to analyze the user tastes (People who liked X, Y, Z tend to like A, B, C) and make recommendations to others accordingly.
Self-driving cars
One of the most widely-discussed deep learning business applications is self-driving cars - a concept every major player has invested in, from Volkswagen (as of 2017) to Google Waymo.
These systems use sensors and a neural network to process a vast amount of data. The car learns how to recognize obstacles and react appropriately, increasing its knowledge through use beyond its factory programming.
The following is how a self-driving car visualizes its environment.
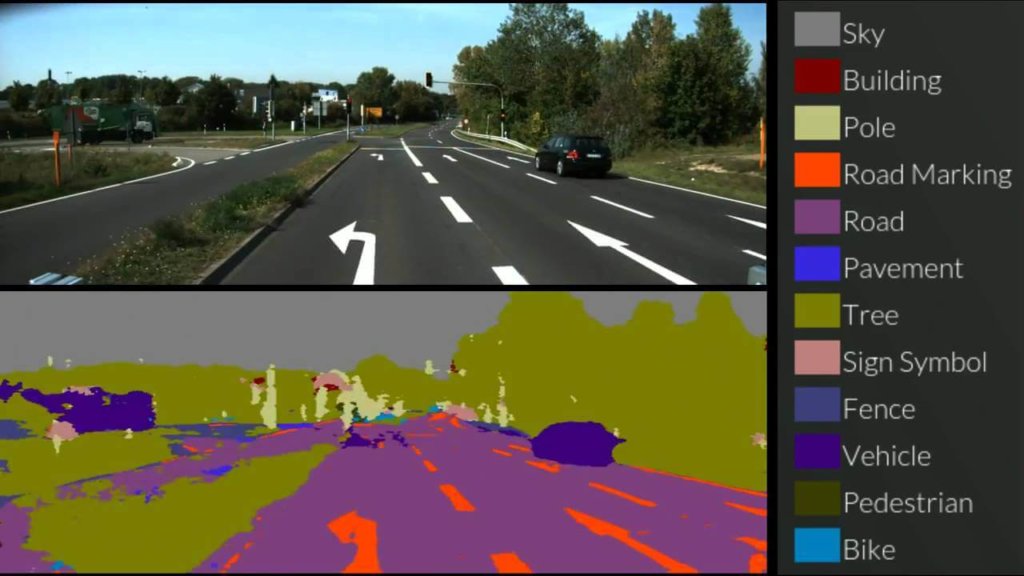
The self-driving car systems use sensors and a neural network to process a vast amount of data. The car learns how to recognize obstacles and react appropriately, increasing its knowledge far beyond its factory programming.
Eventually, given enough data, the machines learn how to drive better than humans. Feedback we have received from operations leaders at manufacturing and logistics companies suggests the same principle applies to their workflow automation - the more historical process data they feed into systems, the better the automation performs.
Image detection and object classification
Another common use is image detection and object classification, as seen with Facebook (as of 2016).
The company has more than enough data on images to work with, making Deep Learning for image detection very accessible.
Currently, Facebook can classify different objects in an image with a very high accuracy.
In fact, you can check it yourself. Right click your own profile picture and pick “Inspect.” You will get a small description bubble with your tags (something like “person. nature. smile”).

Medicine
While there are a lot of potential deep learning business applications in medicine, a big chunk of it is currently in development.
Some of the potential uses could be:
-
Improve diagnosis accuracy - 10-20% of all diagnoses turn out to be inaccurate, as humans, in general, are very prone to error. Deep learning, given enough data, would allow for much higher accuracy. At Tallyfy, we’ve seen healthcare organizations combine deep learning insights with structured clinical workflows to ensure that improved diagnostic accuracy actually translates into better patient outcomes.
-
Gene-tailored medicine - It’s no secret that medicine affects people differently. While something might be perfect for treating one individual, it might cause nasty side effects for someone else. With deep learning, it would be possible to find the right medicine for any specific genetic makeup. While this concept seems more science fiction than reality, there are already companies researching how to make it possible.
-
Map the world - While this might seem more of a long-shot, it’s very much possible. Horus is a company under Nvidia which uses deep learning to help the blind comprehend the world around them. Their product is a headset with a camera, which allows for classifying different objects an individual comes across and conveying the information through the headphones.
Automated translation
If you’ve used Google translate lately, you’ll realize that it’s been getting eerily accurate. What used to be a bunch of jumbled words you would have to decode into English is now, well, working as it should.
The same tech now has a lot more uses - it’s even possible to translate a picture into a different language with your camera.
You might think that the only way this can get better is through real-time translation.
Real-time translation is one of the deep learning business applications teams continue to develop.
Bragi Dash (a pair of headphone-computers) are said to be developed with capability for real-time translation, making language barrier a thing of the past forever.
Want more AI? Check out our article on the Human in the Loop.
About the Author
Amit is the CEO of Tallyfy. He is a workflow expert and specializes in process automation and the next generation of business process management in the post-flowchart age. He has decades of consulting experience in task and workflow automation, continuous improvement (all the flavors) and AI-driven workflows for small and large companies. Amit did a Computer Science degree at the University of Bath and moved from the UK to St. Louis, MO in 2014. He loves watching American robins and their nesting behaviors!
Follow Amit on his website, LinkedIn, Facebook, Reddit, X (Twitter) or YouTube.

Automate your workflows with Tallyfy
Stop chasing status updates. Track and automate your processes in one place.